EIP-2535 Diamond Smart Contract
TLDR;
This article describes how useful the Diamonds standard was to implement Dodao Task management, mint ERC-1155 tokens, connect Diamonds between multiple EVM chains, and call the GitHub Web2 API.
Motivation to Use Diamonds
When starting to develop Dodao.dev, we used the EIP-2535 Diamond standard to create manageable and upgradable smart contracts.
The Diamonds EIP gives you the idea of Diamonds itself and the technology behind it. It is a great booster to get familiar with in-depth Solidity features such as DELEGATECALL, which is used to redirect function calls from the main Diamond contract to its Facets, and storage structs on which Diamond Storage is based.
A Diamond consists of a diamond facade contract and its facets.
Diamonds rely on the feature of DELEGATECALL, which executes the remote smart contract's code in the caller smart contract's storage context.
A -> Diamond -> Facet (delegatecall) msg.sender = A (updates happen on Diamond's storage)
The facade Diamond is usually generic and DELEGATECALLs into its facets for implementation-specific function calls.
Diamond storage relies on Solidity structs that contain sets of state variables that are easy to read and write. A struct can be defined with state variables and then used in a particular position in contract storage. The position can be determined by a hash of a unique string.
Basics of the Approach
The Dodao smart contract is based on the EIP-2535 Diamond-1 reference implementation, which provides a Diamond facade, Diamond init used for facet deployment and upgrades, a DiamondCut facet used for adding and removing facet functions from the Diamond, an OwnerShip facet which maintains contract ownership, and a Louper facet which allows Diamond inspection. The Diamond-1 reference implementation is the generic, not very optimized Diamond implementation that is easy to understand. There are also Diamond-2 and Diamond-3 implementations that optimize Diamond Cuts and Louper functions for different use cases.
The Diamond reference implementation deploy scripts and tests are written for Hardhat. We have modified it to include project-specific facets and added functions for facet add, upgrade, and removal, and exposed it as Hardhat tasks to be used from the CLI. To minimize facet size in order to fit into the 24KB EVM limitation, I have implemented facet library linking and deployment. There is a great hardhat-contract-sizer plugin that allows monitoring your facet sizes.
Additionally, we have added functions to programmatically verify deployed contracts.
The Louper facet allows inspecting Diamonds programmatically both on and off-chain. There is a great project louper.dev which allows Diamond inspection from your web browser.
The Diamonds standard allows for flexible smart contract development by keeping the main Diamond facade contract as a single entry point address and allowing the deployment of required facets when they are ready.
How the Dodao Diamond Looks Like
Dodao.dev is a decentralized and permissionless task marketplace for tech talents and art creators, and relies on several facet and library groups implementing its on-chain functionality, which is constantly being developed and upgraded while keeping the simple and maintainable code structure.
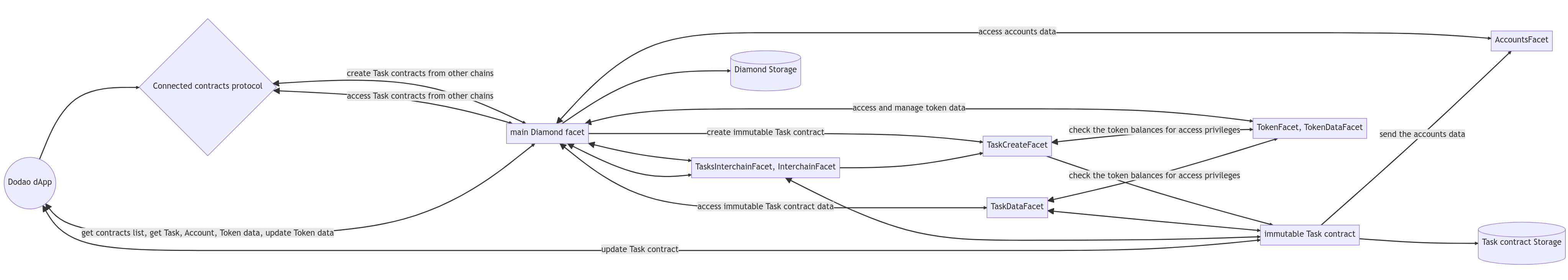
Task and User Account Facets:
TaskCreateFacet.sol - creates non-upgradable Task contracts, which are not linked to the Diamond directly, use their own storage, and use CALLs to push necessary data back to the main Diamond.
TaskDataFacet.sol - contains functions that read Tasks data from the Task contracts created by TaskCreateFacet. It also manages the Task contracts blacklist.
LibTasks.sol and LibTasksAudit.sol - provide underlying functions for the above facets.
LibChat.sol - provides in-Task chat functions.
AccountsFacet.sol - manages user accounts. It is being called by Task contracts when a user participates in or completes the Task. It also manages the Accounts blacklist.
Token Facets:
TokenFacet.sol - creates ERC-1155 compatible fungible and non-fungible (NFT) tokens. Its implementation is based on the Enjin reference implementation rewritten to use Diamond storage and some project-specific functions and features added.
LibTokens.sol - provides underlying functions for the TokenFacet facet.
TokenDataFacet.sol - contains more project-specific functions. Again, with Diamonds, you can easily distribute necessary functions between several facets to maintain the 24KB EVM limitation.
LibTokenData.sol - provides underlying functions for the TokenDataFacet facet.
The only drawback of using a Diamond for ERC-1155 tokens is that only one token ticker (name) can be set for a single contract address. It can be mitigated by creating several Diamonds sharing the same facets.
Connected Contracts Facets:
InterchainFacet.sol - implements the Moonbeam Connected Contracts concept by enabling connection with Axelar/Hyperlane/LayerZero and Wormhole omnichain protocols. The Diamond concept of a facade contract and Diamond Storage for protocol-specific configuration simplified the implementation of the idea to connect contracts between different chains a lot. It is always much easier to know that there is a single static contract address on every chain to be called, which enables better maintainability and security.
LibTokenData.sol - provides underlying functions for the Interchain facet.
LibUtils.sol - provides some generic functions to be reused by multiple facets.
Witnet Oracle Facets:
WitnetFacet.sol - implements the connection with Witnet oracles to query GitHub repository data used to automatically sign Task reviews.
LibWitnetRequest.sol - provides underlying functions for the WitnetFacet facet.
Feel free to clone, fork, reuse, or contribute to the Dodao smart contract diamond.
All the facets use and share several Diamond storages and an AppStorage (it is not recommended to mix Diamond storage and contract storage because of the way Solidity stores data in structs). Diamond storage allows great flexibility in storing and accessing data, as the data at a certain pointer can be accessed from every facet linked to the Diamond.